It is also much faster to access cash information in a cash book than by following the cash through a ledger. A triple-column is an extended version of the double-column the premium tax credit cash book. The bank transactions and the discounts that are given for transactions will be featured in separate ledger accounts in case of single-column cash books.
What is the method of posting a three column cash book into ledger?

The format of a Simple Cash Book is similar to an ledger account, with one amount column on each side. The left-hand side of the cash book is called Debit Side and it records cash receipts and the right-hand side of the cash book is called Credit side and it records cash payments. In next period, it becomes the opening cash balance and is usually termed as balance brought down (balance b/d). A cash book is set up as a subsidiary to the general ledger in which all cash transactions made during an accounting period are recorded in chronological order.
Example of a Simple Petty Cash Book
Contra entries are made when transactions occur between a cash and a bank account, for instance, cash withdrawn from a bank account for business investment. When the ledger clerk receives the cash book, they complete the double-entry process by posting the transactions to other ledger accounts involved in the cash book. Let us understand the format of maintaining a petty cash book or a detailed cash book through the detailed explanation below.
- Because the cash book acts as both; in the journal and ledger, the closing balance of it is directly transferred to the trial balance.
- Payments for which a separate column does not exist are recorded in this column.
- As already stated, a separate cash account in ledger is not opened when a cash book is maintained.
- So, under the double-column cash book, the business also records cash transactions and transactions through the bank.
- When the payee presents the cheque for payment, the drawee verifies the signature and account details before processing the transaction.
Balance Sheet
It records transactions of photocopy, stationery, newspaper, tea, and other miscellaneous expenses. It should be noted that when the cashbook is used as a subsidiary ledger the discount column is still not part of the double entry. The column simply lists the discounts as with any other book of prime entry. Subsequently at the end of the accounting period, the business posts the total of the column to the general ledger discount allowed or received account as appropriate.
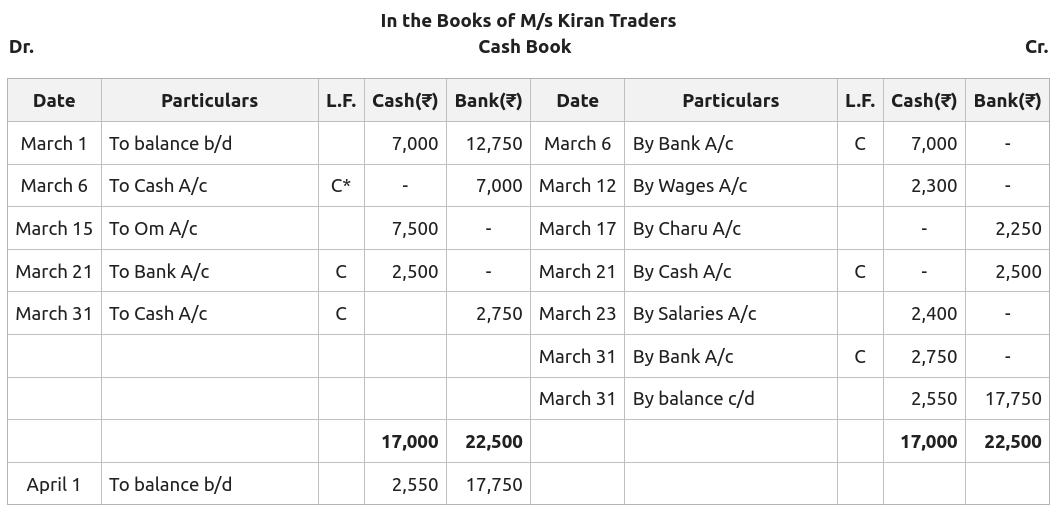
Cash books have two sides (left-hand side and right-hand side) where all receipts in cash are recorded on the left side, and all payments in cash are recorded on the right side. This type of cash book records transactions of three accounts. It has three columns, one for cash, one for the bank, and another one for discounts.
A double-column cash book, also called a two-column cash book, records both cash and bank transactions. So, transactions like cheque payments and bank transfers are recorded in a two-column cash book. Thus, it fulfils the purposes of both a cash and a bank account. Contra entries are not posted because the double entry accounting for these transactions is completed within the cash book. All items on the debit side of the cash book are posted to the credit of respective accounts in the ledger.
These headers are present for both the left side showing receipts and the right side showing payments. In this way, the petty cashier will begin every period with an amount equal to imprest cash, and the amount held by the petty cashier will never exceed this. The amount spent by the petty cashier is reimbursed, thus making up the balance to the original amount.
The balance of cash in a cash book is the total amount of money that is currently in the account. This includes both the money that has been deposited and the money that has been withdrawn. The cash flows will change with every transaction that is recorded in the petty cash book. When money is received, it is recorded in the cash book as a debit. However, there are different types of cash books which can be more complicated.
Cash books resemble the format of ledger accounts and are used to record receipts and payment transactions. Ledger accounts are divided into two parts (the right-hand and left-hand side) to display information. Each cash book contains certain components relevant to identifying transactions and maintaining records. Simple cash book contains only one amount column on each side (debit and credit) for recording cash receipts and cash payments.
Cash books are important because they allow businesses to track their finances in a detailed and organized way. This information can be used to make important decisions about the future of the business. These will provide a detailed overview of the business’ financial health.
A cash book has simplified the entry cash transactions for accounting purpose to a great extent. As it is maintained date wise, any cash payments or the transaction can be correctly traced back in the cash book. Cash book is a special type of book that is only concerned with the recording of cash transactions of an organisation. It performs the dual role of both journal and a ledger for all the cash transactions taking place in a business organisation. This leads to the need for maintaining all cash transactions in one place for the business and necessitates the use of a cash book. In contrast to utilising a cash book template, companies today prefer maintaining records with excel sheets or accounting software.




